
On This Page
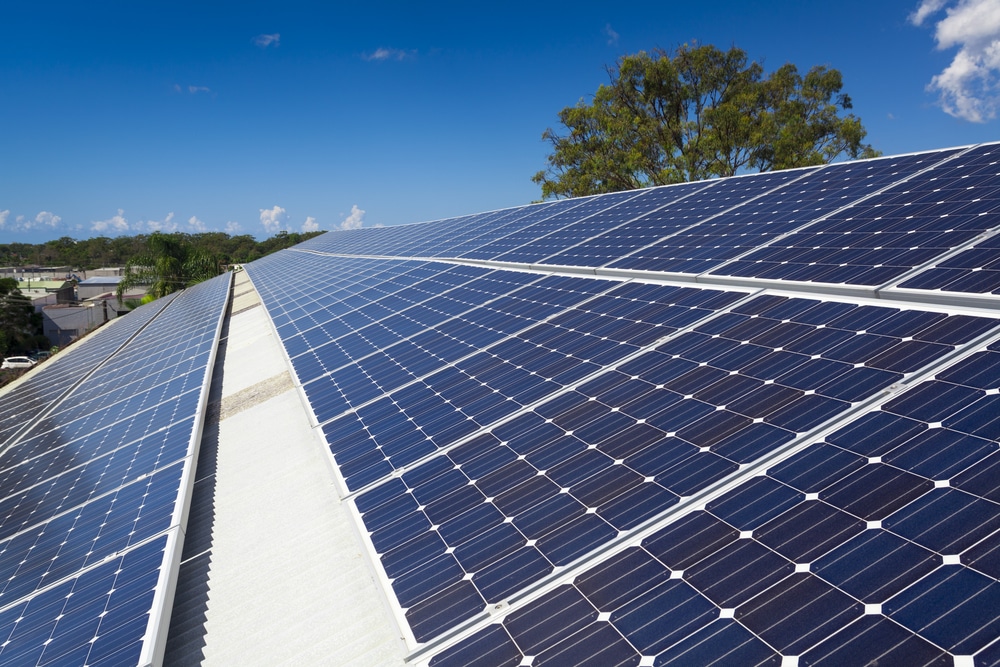
Construction and operating principle of monocrystalline solar panels
Monocrystalline energy storage panels are named after their production processes. Several solar panels contain silicon wafers or cells which contain silicon crystals. The seed is put into pure molten silicon at high temperatures and shaped by melting silicon. A large crystal is split into thin layers to produce solar panels. As long as the cell size is, a typical monocrystalline panel may hold 70 to 82 solar cells.
Performance and features of monocrystalline solar panels
The monocrystalline cells made of the same material as silicon allow for more electron flow, making solar cells more efficient. Monocrystalline panels are efficient and require less space to reach the desired power capacity.
- The pyramidal shape of these solar panel cells provides a more extensive surface area for absorbing more solar energy.
- Metal conductors printed on the cells allow the generated electricity to be collected.
- The cells include a silicon nitride coating to lessen reflection and boost absorption.
- In contrast to the bottom surface, which has a positive electrical orientation, the top surface is diffused with phosphorus, which contributes to the creation of an electrically harmful exposure that contributes to the creation of the electric field.
Check out our page to learn tips and choose the best solar panel.
Characteristics of monocrystalline solar panels
- Dark blue or black appearance
- Feature more pure silicon than other panels
- The panels are highly efficient
- Monocrystalline panels, therefore, take up less roof space
- Longevity is a trait of mono panels
- Monocrystalline panels are typically more expensive.
Monocrystalline solar panels cost
Monocrystalline solar panel prices are higher based on their manufacture. Their increased efficiency and power rating raise their prices. As solar energy has evolved, it is easier to manufacture monocrystalline panels as it becomes easier and cheaper.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of monocrystalline solar panels?
While monocrystalline solar cells offer some advantages and disadvantages, each is discussed in more detail below.
The advantages of monocrystalline solar panels
- They perform effectively in low light conditions, which makes them perfect for cloudy situations.
- These panels are more heat-resistant.
- This type of solar cell is said to have the most extended lifespan, according to the manufacturers, who often offer a 25-year warranty.
- Due to their high efficiency relative to other varieties, they take up less space.
- They have a high level of efficiency.
The disadvantages of monocrystalline solar panels
- When silicon is sliced during manufacturing, a lot of waste material is produced.
- Temperature increases typically harm performance. Comparatively speaking to other solar cell types, it is a slight loss.
- They are only affordable for some because they are pricey solar cells available.
There are various monocrystalline solar panel types
Many types of monocrystalline solar panels are available on the market today. Monocrystalline PERC cells, also known as Passivated Emitter and Rear Contact cells, are becoming increasingly popular. The production capacity of PERC cells is increased by using a modified manufacturing and assembly procedure.
The typical sun cell architecture that has been in use for three decades and is often described in all photovoltaic manuals differs from the solar cell architecture defined by PERC cell technology.
Bifacial solar panels, a different monocrystalline technology, are gaining popularity in commercial ground-mounted applications because they can produce power on both the front and back of a module.
What are Monocrystalline PERC solar panels?
The primary benefit of the PERC cell structure is that it enables manufacturers to produce solar cells with better efficiency than those now possible with traditional solar cells, which are nearing their physical limits. Up to 1%, absolute efficiency improvement is feasible given the level of the technology.
The production process involves different processes, but the increased efficiency reduces prices across the board. The Holy Grail is to increase effectiveness while cutting expenses. Enhancement of solar cell efficiency helps to cut costs.
Therefore, this cell architecture offers one of the finest prospects for generating cost-effective, high-efficiency solar panels.
Definition of bifacial solar panels
Solar electricity is generated via bifacial modules on both sides of the panel. In contrast to standard mono facial opaque-back sheeted panels, bifacial modules show both the front and back of the solar cells.

Image: Lumos Solar’s bifacial solar panels
Some bifacial module manufacturers assert that the additional power produced from the rear can improve production by up to 30% when bifacial modules are mounted on a surface that is highly reflecting (such as a white TPO roof or the ground covered in light-coloured stones).
The designs of bifacial modules are diverse. Some of them have frames, while others don’t. Some have two layers of glass, while others have transparent back sheets. Although there are polycrystalline designs, most use monocrystalline cells. Power is generated from both sides. The only thing that never changes. There are bifacial, frameless dual-glass modules that show the backs of cells. Busbars and contacts are present on the front and rear of the cells in actual bifacial modules.
Energy Matters has a nationwide network of trusted local installers ready to provide you with up to 3 Free Solar Quotes. Complete our quick quiz and begin your solar journey today!









































