Australia, a land rich in natural resources, currently does not utilise nuclear energy for electricity generation. This might seem surprising given the global discourse surrounding nuclear power as a low-carbon energy source. However, Australia’s energy landscape and policy decisions have historically favoured other options.

This comprehensive guide will delve into how nuclear energy generation processes function, explore the theoretical application of nuclear power within an Australian context, and provide an overview of the various nuclear energy systems explained. Understanding these aspects is crucial for discussing Australia’s future energy mix.
On this page
Understanding the nuclear energy generation process
What is nuclear energy?
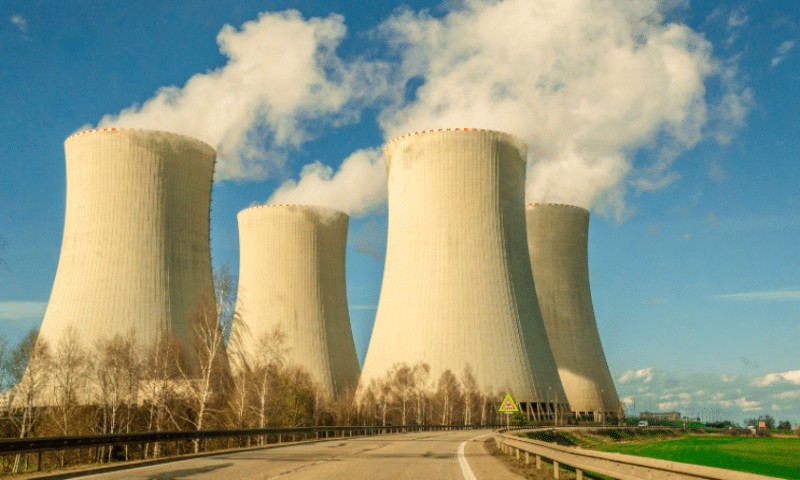
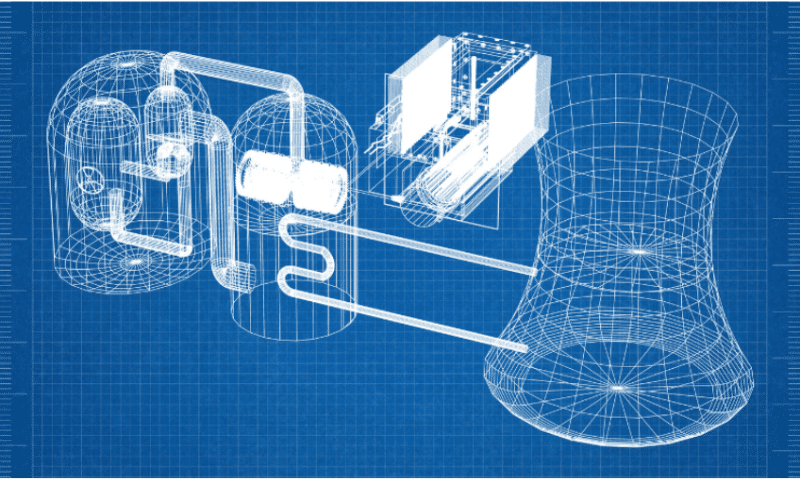
Nuclear energy is produced through nuclear fission, where the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts, releasing a significant amount of energy in the form of heat. This heat is then used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. The primary fuel used in nuclear reactors is uranium, a naturally occurring radioactive element abundant in Australia.
How nuclear power works: A step-by-step overview
To further clarify how nuclear power works, let’s break down the process into key stages:
- Nuclear fission: As described earlier, the core of the process is the splitting of atomic nuclei, typically uranium-235, releasing energy and more neutrons. This controlled chain reaction is maintained within the reactor core.
- Heat generation: The kinetic energy of the fission products and the emitted radiation is converted into thermal energy. This intense heat is used to heat a coolant, usually water, but can also be heavy or molten salt.
- Steam production: The hot coolant circulates through a heat exchanger, transferring its heat to another water loop, causing it to boil and produce high-pressure steam.
- Electricity generation: The high-pressure steam drives a turbine connected to an electrical generator. As the turbine spins, the generator produces electricity through electromagnetic induction.
- Condensation and recycling: The steam is cooled and condensed back into water after passing through the turbine. This water is then pumped back to the heat exchanger to repeat the cycle, improving efficiency.
- Control and safety systems: Maintaining a controlled chain reaction is paramount. Control rods, made of neutron-absorbing materials like cadmium or boron, are inserted or withdrawn from the reactor core to regulate the fission rate. Safety systems are in place to prevent uncontrolled reactions and ensure the integrity of the reactor.
Nuclear energy systems explained
There are various types of nuclear reactors, each with unique designs and operational characteristics:
- Pressurised Water Reactors (PWRs): Use high-pressure water as coolant and moderator.
- Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs): Boil water directly in the reactor core to produce steam.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): Compact reactors designed for modular construction, offering flexibility and scalability.
- Generation IV Reactors: Advanced designs focusing on sustainability, safety, and efficiency.
Explaining the nuclear fuel cycle
The nuclear fuel cycle is a process that takes place in producing nuclear energy. It uses uranium to create heat, which is then used to generate electricity.
The first step in the nuclear fuel cycle is mining. Uranium is mined from the ground and then transported to a processing facility. Uranium is a radioactive metal found in small amounts in most rocks and soils. Once mined, the uranium ore is transported to a processing plant.
The uranium is enriched at the processing facility, which means it is made more radioactive. At the processing plant, the uranium ore is crushed and ground up. This process separates the uranium from other metals in the ore.
The uranium is then converted into a gas called Uranium Hexafluoride (UF). The enriched uranium is then used to create fuel rods used in nuclear reactors. Enriched uranium has a higher concentration of the isotope uranium-235. This is the isotope that is used in nuclear reactors to create energy.
After enrichment, the uranium is turned into fuel pellets. These pellets are then loaded into fuel rods and placed in a reactor. In the reactor, the uranium-235 atoms split apart. This process releases energy that is used to generate electricity.
After the uranium fuel is used, it is removed from the reactor. The fuel pellets are then reprocessed to remove any radioactive waste. This waste is then disposed of in a safe location.
The dangers of nuclear waste
Nuclear waste is incredibly dangerous to human health. It can cause cancer, birth defects, and various other health problems. Even small amounts of nuclear waste can be harmful to human health.
Nuclear waste can come from various sources, including power plants, nuclear weapons facilities, and medical facilities. Nuclear waste can also come from accidents at these facilities. For example, the Chernobyl disaster released large amounts of nuclear waste into the environment.
Nuclear waste can stay in the environment for centuries. It can contaminate the air, water, and soil. It can also contaminate plants and animals. Nuclear waste contaminates food or water and can cause serious health problems for people who consume those products.

How is nuclear waste disposed of?
There are two main methods of disposing of nuclear waste: underground storage and above-ground storage.
Underground storage is considered to be the safest method of disposal. The waste is buried deep underground, where it will not come into contact with the environment. Above-ground storage is less safe, as the waste is stored in containers that could leak or break.
Is nuclear energy renewable or nonrenewable?
Nuclear power is a hot topic of debate these days. Some people believe it is a renewable energy source, while others think it is not.
The truth is nuclear power can be either renewable or non-renewable.
Nuclear power facilities generate renewable electricity, but the fuel used to generate that energy is not. Nuclear plants work by using uranium to generate heat. This heat is then used to create steam, which turns turbines and generates electricity.
The problem with this method is that uranium is a non-renewable resource. Once it is used up, it cannot be replenished. This means that nuclear power plants can only operate for a limited time before they need to be shut down.
Energy Matters has been operating in the renewable energy industry since 2005. Energy Matters has a nationwide network of trusted local installers ready to provide you with up to 3 Free Solar Quotes. Complete our quick quiz and begin your solar journey today!
Nuclear fusion
There is another way to generate nuclear power that does not use uranium, though science has not yet produced a way to practically harness or utilise this method. This method, known as fusion, uses hydrogen instead. Hydrogen is a renewable resource, which means that it can be used over and over again.
Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two atoms to form a new, heavier atom. This process releases massive amounts of energy, which can be harnessed to generate electricity. Fusion power plants would produce no greenhouse gases, no radioactive waste, and would be virtually limitless in generating energy.
The sun is powered by nuclear fusion, and scientists have worked to develop a way to harness this energy on Earth for decades. The challenge lies in creating the conditions necessary for nuclear fusion to occur. Scientists are still working to perfect this technology, but there is great hope that nuclear fusion could one day provide a clean, renewable energy source for the world.
Problems with nuclear energy are released
Nuclear energy is one of the most polarising issues in the world today. Supporters say it is a clean and efficient way to produce energy, while opponents argue that the dangers of nuclear accidents are simply too high. Let us take a closer look at the nuclear power plant sites such as Chernobyl and Fukushima and how they became nuclear disasters.
Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster
There is no question that nuclear accidents can have devastating consequences. The most famous nuclear accident in history is the Chernobyl disaster, which occurred in 1986 in Ukraine. The accident resulted in the release of large amounts of radiation into the atmosphere, which contaminated large areas of Europe. Hundreds of people were killed, and thousands more were exposed to dangerous radiation.
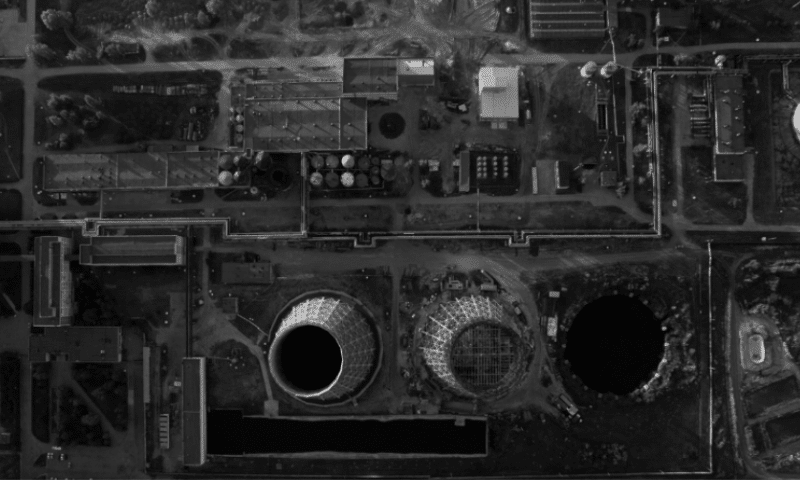

While the Chernobyl disaster was a tragedy, it is important to remember that it was also an isolated incident. Most nuclear power plants worldwide have operated without incident for decades. However, this does not mean that nuclear accidents are impossible.
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster
In 2011, a massive earthquake and tsunami caused a nuclear meltdown at Japan’s Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. The accident resulted in the release of large amounts of radiation into the environment and forced the evacuation of hundreds of thousands of people.
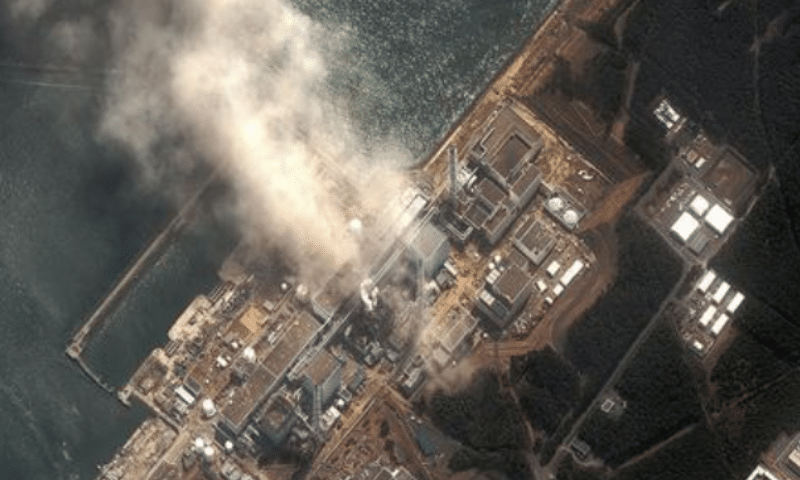

The Fukushima disaster was a wake-up call for the nuclear industry. It showed that even the most well-designed nuclear power plants could be vulnerable to natural disasters. This is why many experts have called for a rethink of how we generate nuclear energy.
What happens if a reactor meltdown occurs?
A nuclear reactor meltdown is a catastrophic failure of the reactor core. The resulting release of radioactive materials can pose a serious health and environmental hazard. A meltdown can occur for many reasons, including operator error, natural disasters, or terrorist attacks.
When a meltdown occurs, the first thing that happens is that the fuel rods in the reactor core begin to overheat. This can cause the fuel rods to melt, and in some cases, the molten fuel can breach the containment vessel and escape into the environment.
Radioactive materials can be released into the air, water, and soil if this happens. These materials can then be inhaled or ingested by people and animals and can cause various health effects, including cancer.
What are the risks of nuclear energy?
There are several problems with nuclear energy that make it dangerous.

Radioactive waste
First, there is the issue of radioactive waste. Nuclear power plants produce large amounts of radioactive waste that must be carefully stored and monitored for centuries. If this waste is not properly managed, it could leak into the environment and cause serious health problems for people and animals.
Nuclear proliferation
Second, there is the risk of nuclear proliferation. Nuclear power plants use enriched uranium, which can be used to make nuclear weapons. If nuclear weapons were to fall into the hands of terrorists or rogue states, they could be used to devastating effect.
Nuclear accidents
Finally, there is the danger of nuclear accidents. As we have seen, even the most well-designed and operated nuclear power plants can experience accidents. These accidents can release large amounts of radiation into the environment and cause widespread damage.
Nuclear energy: The latest developments
Nuclear energy has been in the news lately, and for a good reason. The latest developments in the field can forever change how we generate power.
The first new development is Small Modular Reactors (SMRs). SMRs are nuclear reactors that are significantly smaller than traditional nuclear power plants. This makes them much cheaper to build and operate.
SMRs can be built in a factory, which reduces construction costs even further.
One of the benefits of SMRs is that they can be used to generate power in remote areas. This is because they do not require much land, water, or other resources.
SMRs can be turned on and off as needed, which makes them much more flexible than traditional nuclear reactors.
The second new development is thorium-fueled reactors. Thorium is a radioactive element that can be used to fuel nuclear reactors. Thorium-fueled reactors have several advantages over traditional nuclear reactors. Thorium is more abundant than uranium, so it is cheaper to use as a fuel source.
Thorium produces less waste than uranium, and the waste it does produce is less radioactive.

Powering Australia's future
Understanding how nuclear energy works is essential for evaluating its potential role in Australia’s energy future. While nuclear power offers a low-emission energy source, challenges related to cost, waste management, and public acceptance must be addressed.
The anti-nuclear lobby would much prefer more focus on solar power and wind energy as better renewable sources to address the world’s current and future energy needs. They say that the safest reactor is the one that is 148,000,000 km away. You can use that reactor for everyday energy by getting a solar power system today.
Are you looking to save money on your electricity bills and reduce your carbon footprint? Solar energy is the perfect solution!
Energy Matters is here to guide you every step of the way. Energy Matters is one of Australia’s most trusted solar quotes due to our high customer satisfaction and industry recommendations. Our team of solar experts can help you get up to 3 FREE solar quotes from pre-qualified and vetted solar firms in your area.