If you’ve installed solar panels and are generating your electricity, reading your solar energy bill should be simple, right? Not always.
For many Australians, understanding solar charges and how solar energy credits appear on electricity bills can be confusing. In this guide, we’ll break down your solar energy bill, explain each section, and help you take full advantage of your solar system’s financial benefits.
Understanding the basics of your Australian solar energy bill
Before diving into the specifics of solar charges and credits, let’s cover the fundamental sections standard to most Australian energy bills.
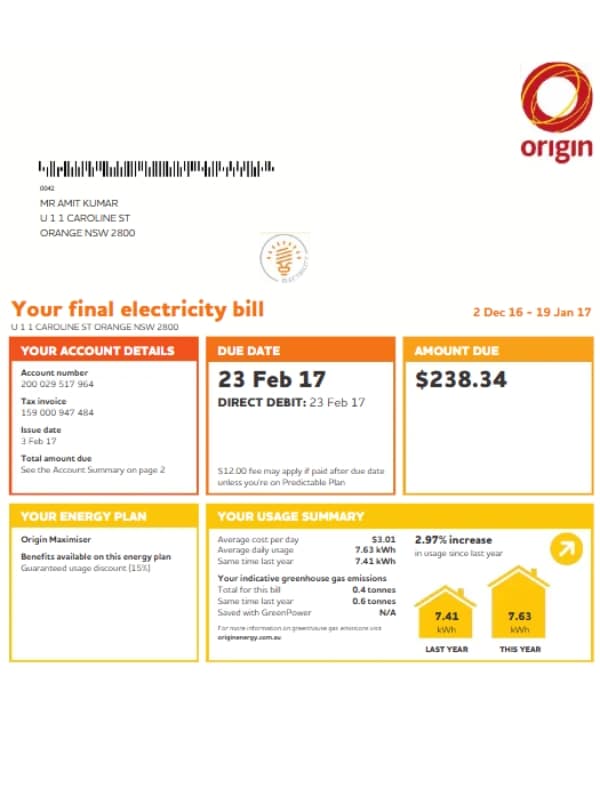
- Customer and account details: This section typically includes your customer number, account number, service address, billing period dates, and contact information for your retailer and distributor. These details are essential for any communication regarding your bill.
- Billing period: This indicates the start and end dates of the period for which you are being charged. It’s often expressed in days, typically 30 or 90 days for monthly or quarterly bills.
- Meter readings: Your bill will show readings from your electricity meter. These can be “actual” readings taken by a meter reader or “estimated” readings if access wasn’t possible. Always check if an estimate was used, as you can submit your reading if you have a smart meter.
Understanding electricity charges vs. solar credits
In some cases, you might see negative bills (bills in credit) if your solar credits exceed your grid usage. That means your system is performing very efficiently. When reviewing your solar bill, it’s important to differentiate between electricity charges (aka solar charges) and solar credits:
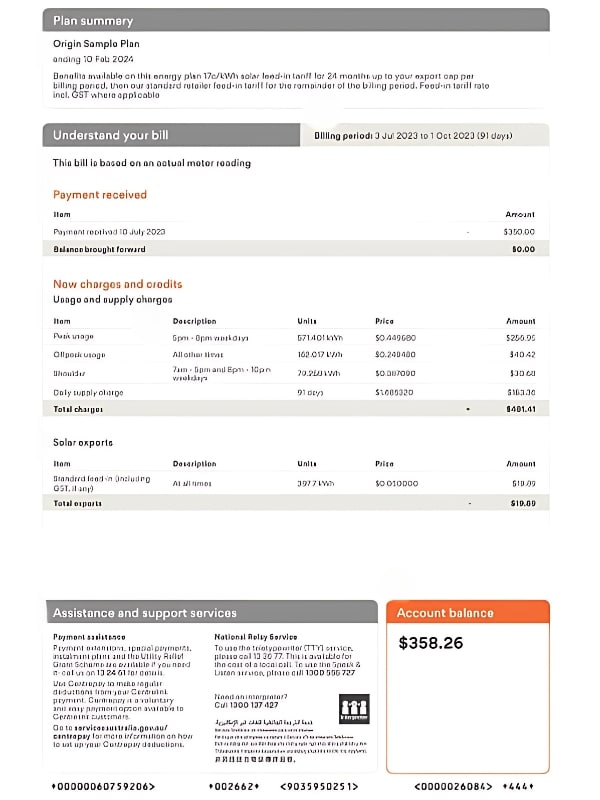
- Electricity charges: Any costs associated with energy consumption beyond your solar output. This includes electricity from the grid, daily supply charges, and off-peak usage.
- Solar credits: Earned from the energy your solar panels generate and feed back into the grid.
Source&Images: Origin
Breaking down solar charges and credits
The heart of your solar energy bill explanation lies in understanding how the solar power you generate interacts with your grid usage. This involves several key terms and calculations.
Electricity usage charges: What you pay for from the grid
Even with solar panels, you will likely still draw electricity from the grid, especially at night or on cloudy days. These are your electricity usage charges.
- Supply charge (daily charge): This is a fixed daily fee charged by your electricity distributor for maintaining the grid and delivering electricity to your property, regardless of the amount of electricity you use. This charge contributes to the infrastructure that connects your home to the broader network.
- Usage charges (variable charges): These charges are based on the amount of electricity (measured in kilowatt-hours, kWh) you consume from the grid. The rate per kWh can vary significantly depending on your tariff plan.
- Flat rate (single rate) tariff: You pay the same rate per kWh for electricity used from the grid, regardless of the time of day. This is the simplest tariff structure.
- Time-of-Use (TOU) tariff: With a TOU tariff, the rate you pay for electricity from the grid varies depending on the time of day. Typically, there are peak (highest rate), shoulder (medium rate), and off-peak (lowest rate) periods. Running energy-intensive appliances during off-peak times can significantly reduce your bill with this tariff.
- Controlled load tariff: This tariff applies to specific appliances (like electric hot water systems or pool pumps) connected to a separate meter circuit. These appliances are usually supplied with power during off-peak hours at a lower, dedicated rate.
- Demand charge tariff: Some plans include a demand charge, which is based on the highest amount of power (in kilowatts, kW) you draw from the grid during a specific peak period within the billing cycle. This encourages consistent usage rather than large, sudden spikes in consumption.
How to read your solar energy bill: A step-by-step guide
Your solar energy bill is usually split into several sections. Here’s a breakdown of what to look for:
1. Account summary
This section provides a snapshot of the following. It may also display any carry-over credits from previous months.
- The total amount due
- Payment due date
- Billing period
2. Meter readings and usage
Ensure the meter readings match the data from your solar inverter for accuracy. This section will typically detail:
- Total electricity consumed from the grid (kWh)
- Solar electricity exported to the grid (kWh)
- Net electricity usage (kWh = grid usage – export)
3. Feed-in tariff credits
If you’re not seeing feed-in tariff credits, it may indicate an issue with your meter or energy plan. This indicates:
- The amount of energy you exported
- The tariff rate per kWh
- Total feed-in credit earned
4. Electricity charges
Compare this section with your solar system output to assess whether your system offsets enough of your power usage. Here’s where you can find:
- Grid electricity costs
- Daily supply charges
- Other service fees (if any)
5. Solar system performance summary
Utilise this information to optimise energy usage during peak solar hours. Some providers include graphs or summaries that display:
- Daily or monthly solar generation
- Export vs. consumption rates
- Seasonal performance trends
Common issues to look out for
If you notice discrepancies, get in touch with your energy provider or your solar installer. You can also use energy monitoring tools to verify your consumption and export figures. Understanding your solar energy bill involves identifying errors or inefficiencies. Keep an eye out for:
- Incorrect feed-in tariff rates
- Missing export data
- Mismatched solar production and export values
- Unexpectedly high grid usage
Tips for managing your solar energy bill effectively
Here are some practical ways to optimise your savings:
- Shift your power usage
Use energy-efficient appliances, such as washing machines or dishwashers, during peak solar production hours (10:00 a.m.–2:00 p.m.). - Regularly monitor your solar inverter
Your solar inverter shows real-time solar generation. Use this to match your usage habits. - Switch to a better solar plan
Not all electricity retailers offer the same feed-in tariffs. Compare plans to maximise your returns. - Check for hidden charges
Some energy plans with high feed-in tariffs may also have higher daily supply charges. Look at the complete bill to understand the trade-offs. - Upgrade your system if needed
If your energy usage has increased (e.g., due to electric vehicle charging), it may be time to add more solar panels or a battery.
Powering up your EV with solar
If you plan to purchase an EV, integrating an EV charger into your solar system is a great way to “fuel” your car with clean, renewable energy.
Solar billing with a solar battery system
Understanding your solar bill when a solar battery storage system is installed requires monitoring both solar generation and battery usage patterns. If you have a solar battery:
- You may reduce grid usage even further.
- Your export rates might decrease as you store more energy instead of sending it to the grid.
Use Energy Matters’ easy-to-use solar power and battery storage calculator to determine the size of your solar system with storage! Our solar calculator will generate performance information and potential savings.
We can send this information to 3 of our pre-vetted and trusted local installers in your area to receive obligation-free solar quotes and take the first step towards true energy independence!

Making the most of your solar setup
Your solar energy bill is more than just a monthly payment—it’s a tool to manage and optimise your solar investment. Take control by understanding solar charges, tracking your energy habits, and choosing the right plan. Don’t just pay your bill – understand it and make it work for you!
At Energy Matters, we’re here to support every step of your solar journey—compare quotes, explore smarter energy plans, and maximise your solar savings today!




















































