Australia’s climate journey is a compelling narrative of resilience and adaptation. From ancient shifts to modern challenges, understanding the history of climate change in Australia is crucial. This exploration examines the timeline of climate change, highlighting significant climate events that have shaped the nation’s environmental and societal landscapes.

At Energy Matters, we believe knowledge is power. Stay informed, act smart, and join the renewable energy revolution today to protect our future.
On this page
Early climate variations in Australia
Long before industrialisation, Australia experienced natural climate fluctuations. Geological records and paleoclimate studies, analysing ice cores from Antarctica and sediment samples, indicate periods of warmer and cooler temperatures over millennia. These natural cycles were driven by factors such as changes in Earth’s orbit, solar activity, and volcanic eruptions.
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, with their deep connection to the land spanning tens of thousands of years, possess invaluable traditional ecological knowledge about these environmental shifts. Their oral histories and cultural practices often reflect adaptations to past climate variability.
Did you know Energy Matters is Australia’s largest renewable news, blog and educational resource? Subscribe to Energy Matters’ weekly newsletter and keep updated even with incentives, rebates and recommended solar product offers.
The onset of anthropogenic climate change
The late 19th and early 20th centuries mark a turning point in Australia’s climate history, particularly in terms of climate change. The Industrial Revolution, with its increasing reliance on fossil fuels, led to a gradual rise in global greenhouse gas emissions. While the initial impacts in Australia were less pronounced, the seeds of future warming were sown. Scientific observations began to document a slow but steady increase in average temperatures across the continent. This period laid the foundation for the more rapid changes observed in recent decades.
Significant climate events: A timeline of change
Australia’s climate change timeline is marked by increasingly frequent and intense significant climate events. These events serve as stark reminders of the escalating impacts of global warming.
- Late 1800s – Early 1900s: A gradual warming trend was observed, although it was not yet widely recognised as anthropogenic. Early meteorological records begin to show subtle shifts in temperature averages.
- Mid-20th century: Increased awareness of rising global temperatures and the potential role of human activities. Scientific research is increasingly focusing on the climate systems of the Southern Hemisphere.
- Late 20th century: More frequent heatwaves and drought conditions became apparent in many parts of Australia. The scientific consensus on anthropogenic climate change begins to solidify internationally.
- Early 21st century: Australia experiences some of its hottest years on record. The Millennium Drought, which occurred from approximately 1997 to 2009, severely impacted agricultural regions and water resources, underscoring the continent’s vulnerability to prolonged dry periods.
- The 2009 Black Saturday bushfires in Victoria resulted in a significant loss of life and property, underscoring the increased fire risk associated with hotter and drier conditions.
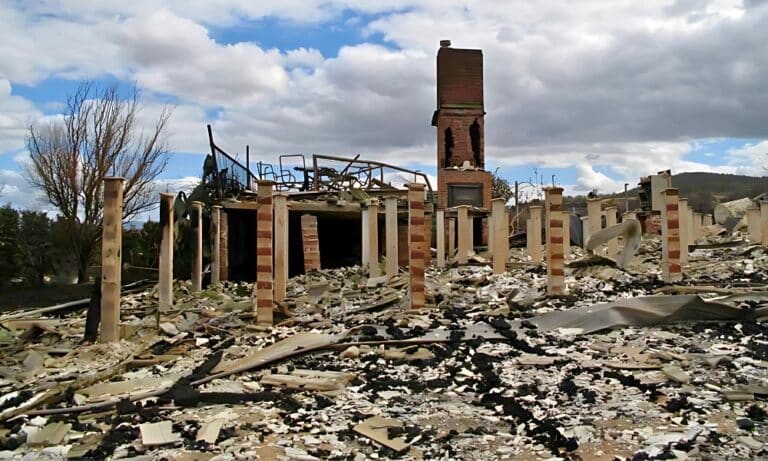


Source & Images: National Museum of Australia – Black Saturday bushfires

- 2010-2012 La Niña events: While bringing significant rainfall and flooding to some areas, these events also highlighted the intensification of extreme weather under a changing climate.
Image: Australian Government Bureau of Meteorology – Explainer: What is a La Niña?
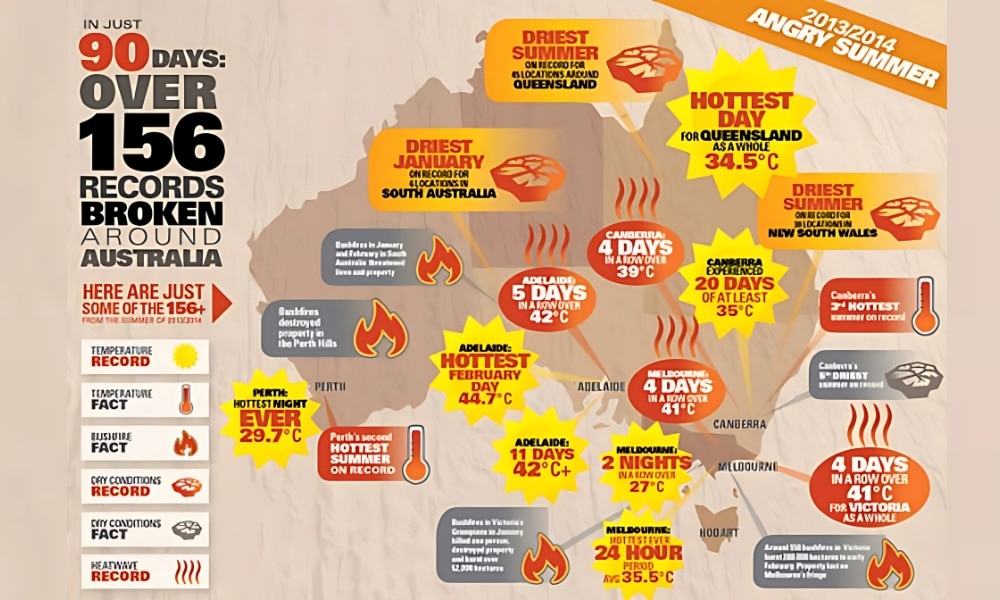
- 2013 “Angry Summer”: Australia experienced a prolonged period of record-breaking heat waves across multiple states, with numerous temperature records broken.
Image: Climate Council – What Does Climate Change Mean for Your Local Area?
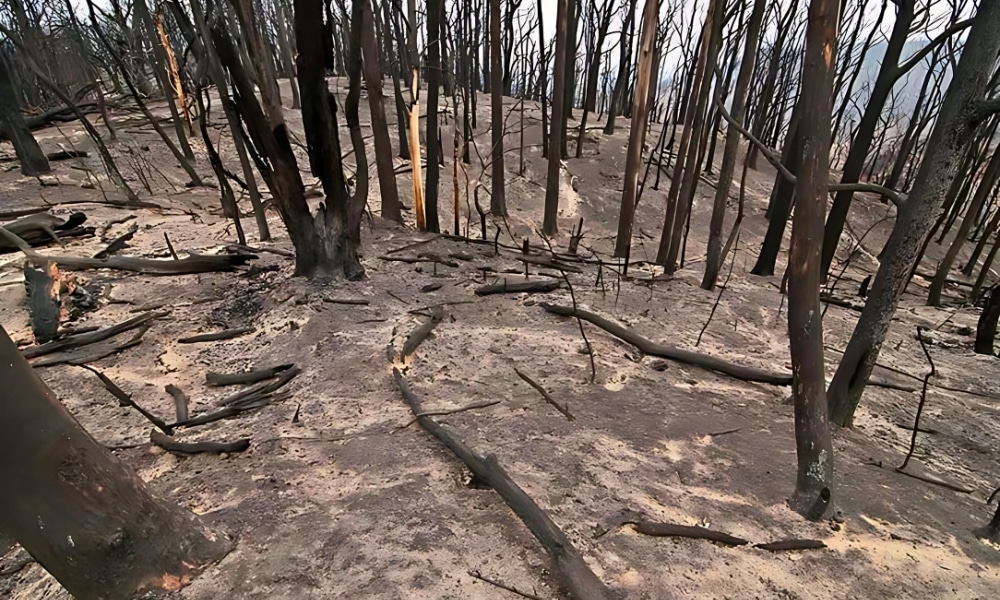
- 2019-2020 Black Summer Bushfires: Unprecedented bushfires ravaged vast areas of Australia, causing immense ecological damage, significant air pollution, and further highlighting the link between climate change and extreme fire weather. An estimated 3 billion animals perished or were displaced.
- Recent years (2021-present): Continued trends of rising average temperatures, more frequent and intense heatwaves, and altered rainfall patterns. The Great Barrier Reef continues to experience mass coral bleaching events due to warmer ocean temperatures.
Current climate change statistics and figures for Australia
Up-to-date data paints a clear picture of the ongoing impacts of climate change in Australia.
- Temperature increase: Australia’s average surface temperature has increased by approximately 1.51 ± 0.23 °C since national records began in 1910 (State of the Climate 2024 report, Bureau of Meteorology and CSIRO). This warming trend is consistent with global climate change.
- Sea level rise: Global average sea levels have risen by approximately 21-24 cm since 1880, with the rate of increase accelerating in recent decades (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Sixth Assessment Report). Australia’s coastal regions are increasingly vulnerable to coastal erosion and inundation.
- Extreme heat: The frequency of extreme heat events has increased significantly. The number of days with temperatures exceeding 35°C has increased across many parts of the country.
- Rainfall patterns: Rainfall patterns are changing, with a long-term decline in average rainfall observed in the southeastern and southwestern parts of Australia. This has significant implications for water security and agriculture.
- Ocean warming and acidification: Ocean temperatures around Australia are rising, contributing to coral bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef and other marine ecosystems. The absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the ocean is also contributing to ocean acidification, a phenomenon that poses a significant threat to aquatic life.
- Greenhouse gas emissions: Australia’s national greenhouse gas emissions in the year to December 2023 were estimated to be 458.6 Mt CO₂-e (Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water). While there are efforts to reduce emissions, further action is crucial.
The future implications of climate change in Australia
The climate change timeline suggests that without significant and rapid reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, the impacts on Australia will continue to intensify. Projections indicate more frequent and severe heatwaves, longer and more intense droughts, increased bushfire risk, and further sea level rise.
These changes will have profound consequences for human health, infrastructure, agriculture, natural ecosystems, and the Australian economy. Understanding the history of climate change is vital for preparing for these future challenges.
Policy responses and climate action
Australia’s approach to climate change has evolved:
- Royal commission report: Following the Black Summer fires, a report emphasised the need for urgent climate reform to mitigate future natural disasters.
- Youth activism: The 2019 student climate strikes mobilised up to 300,000 participants, highlighting public demand for more decisive climate action.
Sources: Australian Government Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water – Understanding Climate Change | WWF Australia – Climate | State of the Environment Australia – Climate change and extreme events | Australian Museum – Impacts of Climate Change | SBS News Australia – The recent history of Australia’s climate change wars
Addressing climate change: A call to action
The evidence is clear: climate change is real, it is happening now, and human activities are the primary driver. The significant climate events of Australia’s past and present underscore the urgency of taking meaningful action. We must transition towards cleaner energy sources, implement sustainable practices, and build resilience to the unavoidable impacts of climate change.
Energy Matters urges you to embrace a sustainable future. Explore renewable energy options, adopt energy-efficient practices, and advocate for climate action. The time to act is now to safeguard Australia’s future for generations to come.
Energy Matters has been recognised for our continued excellence in the Australian solar industry. We provide our customers with high-quality resources, insight, and access to reputable solar quotes.
Our team of solar experts can help you get up to 3 FREE solar quotes from pre-qualified and vetted solar firms in your area.