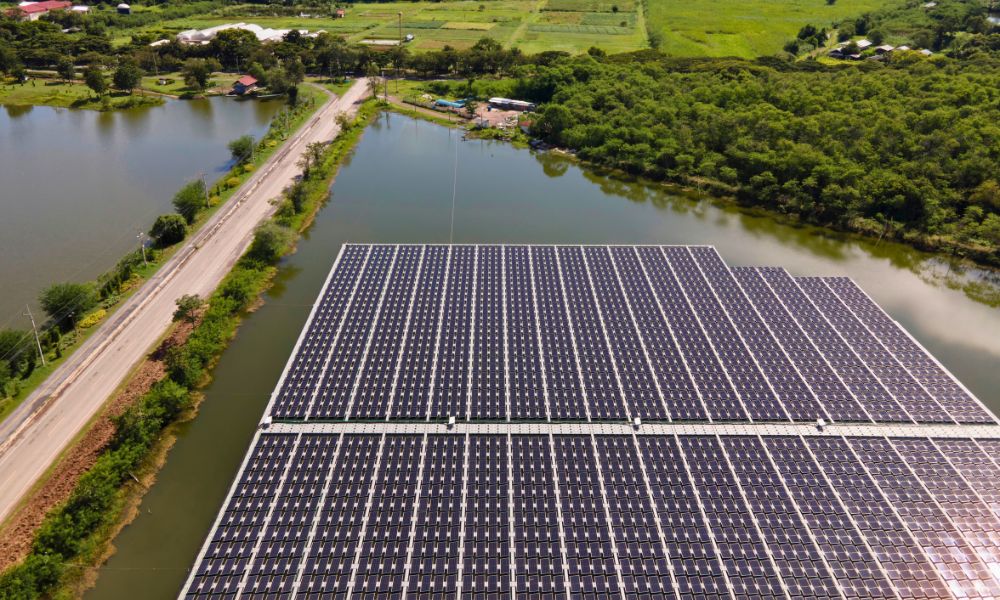
In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy sources, solar energy has emerged as a promising solution to combat climate change and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. Over the years, solar panels installed on rooftops and vast open fields have become familiar sights. However, an innovative approach is gaining momentum, offering new possibilities for harnessing an infinite amount of the sun’s energy: floating solar energy.
In this article, we delve into the concept of floating solar and explore its potential, highlighting the recent developments mentioned in the article by PhD Candidate, School of Engineering, David Silalahi and Professor of Engineering Andrew Blakers both in Australian National University published in The Conversation.
Energy Matters has been a leader in the renewable energy industry since 2005 and has helped over 40,000 Australian households in their journey to energy independence.
Let us discuss and choose the best quote that suits your needs and budget, and we can connect you with our trusted local installers, who will provide up to 3 FREE solar quotes for your home and business solar energy system.
Global projects and insights: The rise of floating solar installations
Understanding floating solar panels
Floating solar, also known as floating photovoltaic (FPV) or floating solar farms, involves the installation of solar panels on water bodies such as lakes, reservoirs, and even offshore waters. The concept is not entirely new, as early experiments with floating solar date back to the 1970s. However, recent advancements in technology and growing environmental concerns have sparked renewed interest in this approach.
Indonesia has significant water-based solar energy potential
A groundbreaking new research study reveals that vast arrays of offshore solar panels floating on calm equatorial seas have the potential to revolutionise energy production in densely populated countries in Southeast Asia and West Africa. By harnessing the abundant solar energy available in these regions, it is estimated that Indonesia alone could generate a staggering 35,000 terawatt-hours (TWh) of solar energy annually, equivalent to the current global electricity production.
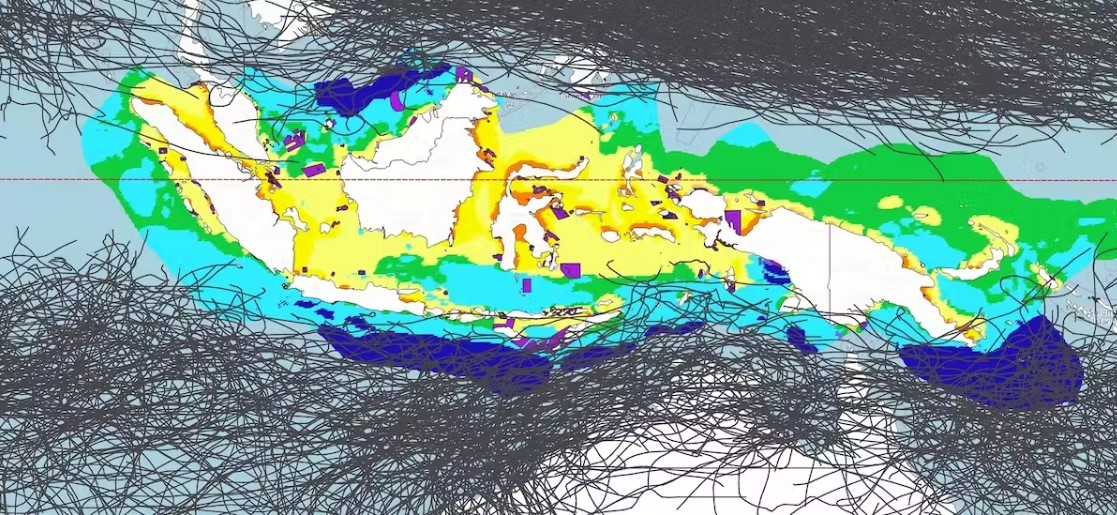
Unlike wind energy, which is limited in these tropical locations, offshore floating solar panels present an ideal solution to address the solar energy needs of high population density countries like Indonesia and Nigeria. Furthermore, global heat maps show that the Indonesian archipelago and the Gulf of Guinea near Nigeria have the greatest potential for floating solar arrays.
The research suggests that the global economy will be significantly decarbonised and electrified by mid-century, with solar and wind energy playing a pivotal role. Approximately 70 square kilometres of solar panels could fulfil the solar energy requirements of one million affluent individuals in a zero-carbon economy, and these panels can be deployed on rooftops, in arid areas, or even floated on water bodies.
While land-based solar options may be limited in highly populated regions, offshore floating solar offers an attractive alternative, especially in regions that experience calm seas with minimal waves and winds. Such areas could generate up to one million TWh per year, exceeding the solar energy needs of a fully decarbonised global economy supporting 10 billion affluent people by five times.
Australia's untapped potential for water-based solar energy
Australia’s vast network of dams, reservoirs, and mine pit lakes provides a substantial opportunity for deploying water-based solar energy. Regions facing water scarcity, such as South Australia and Western Australia, stand to gain significantly from reduced evaporation and increased energy production.
- High solar irradiance: Australia’s sunny climate ensures maximum energy capture from solar installations.
- Reservoirs and dams: Large reservoirs and dams, essential for water storage, can also accommodate floating solar farms, maximising the utilisation of existing infrastructure.
- Coastal applications: While more complex, exploring the feasibility of floating solar installations in sheltered coastal areas could further expand Australia’s renewable energy capacity.
While the offshore floating solar industry is still in its early stages, the research indicates that regions within 5-12 degrees of latitude of the Equator, particularly in and around the Indonesian archipelago and the Gulf of Guinea, hold the most promise for this technology. These areas boast low wind generation potential, rapid population growth, and considerable intact ecosystems that should not be cleared for solar farms. Additionally, tropical storms rarely impact equatorial regions, reducing the risk of damage to the floating panels.
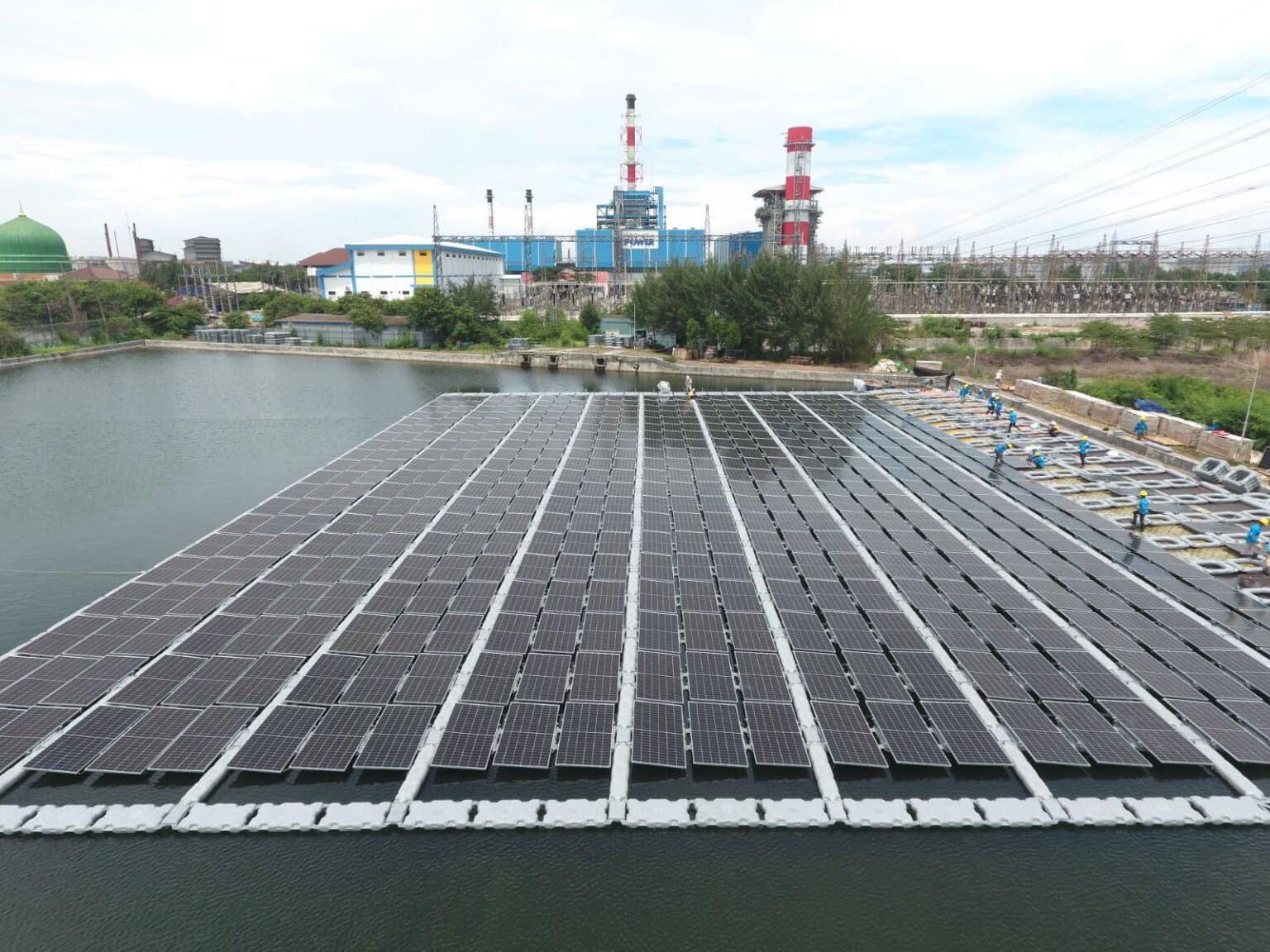

Challenges and future prospects
Despite some challenges, such as salt corrosion and marine fouling, the study predicts that offshore floating solar panels will play a vital role in the solar energy mix for countries with access to calm equatorial seas. By mid-century, it is projected that approximately one billion people in these regions will primarily rely on solar energy, marking one of the fastest solar energy transitions in history. As the offshore floating solar industry matures, this innovative technology offers a promising and sustainable solution to meet the solar energy demands of rapidly growing populations in Southeast Asia and West Africa.
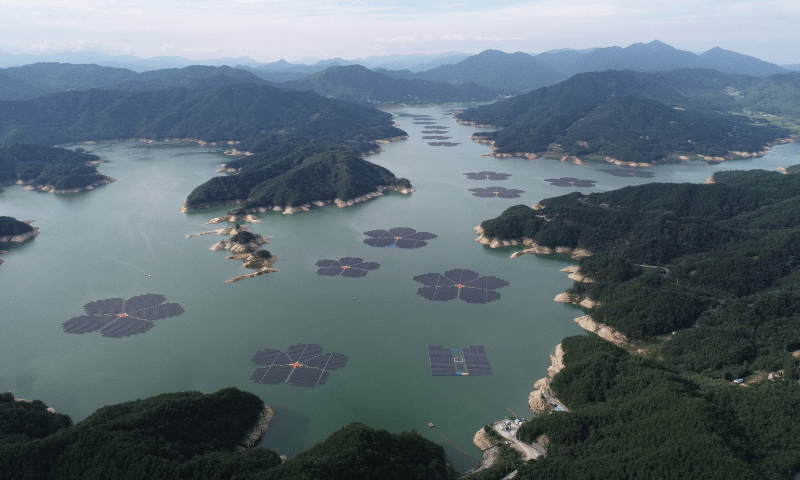

Is solar energy suitable for your business? Solar energy has numerous advantages that are worth investigating. Investing in solar will minimise your operational costs, reduce your company’s carbon footprint, and prepare it for the future. A commercial property with a solar installation is excellent for business.
When installing commercial solar for a company, it is crucial to be informed of all types of federal government solar rebates, incentives and the many benefits these provide, as they may help Australian businesses become future-ready and sustainable for years to come.
Contact us today for up to 3 FREE quotations from commercial solar firms we’ve pre-qualified and vetted for their track record of delivering Australia’s best business solar systems.
Some key benefits of floating solar farms
- They can generate electricity even when the sun is not directly overhead.
- They can be installed in areas that are not suitable for other types of solar energy projects.
- Reduced water evaporation: They have several environmental benefits, such as reducing evaporation and cooling water bodies.
- Algae control: Shading water surfaces can inhibit algal blooms, improving water quality and ecosystem health.
- Enhanced efficiency: The cooling effect of the water helps reduce the solar panels’ operating temperature, leading to increased energy output. Lower temperatures improve the efficiency of photovoltaic cells, boosting overall power generation.
- Grid proximity: Many reservoirs are located near existing grid infrastructure, simplifying the connection and reducing transmission losses.
The future of floating solar farms in Australia
With technological advancements and increasing awareness of its benefits, floating solar installations are poised to play a pivotal role in Australia’s renewable energy transition. As the technology matures and costs decline, widespread adoption is expected.
- Hybrid systems: Integrating floating solar installations with other renewable energy sources, such as hydropower, can create hybrid systems that provide a stable and reliable power supply.
- Community-based projects: Implementing smaller-scale floating solar installations in local communities can empower residents and promote decentralised energy generation.
- Research and development: Continued investment in research and development is crucial to improve water-based solar energy technologies’ efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
An infinite amount of clean solar energy
Floating solar power represents a transformative step towards achieving a sustainable future with limitless clean solar energy. As the world continues to face the pressing challenge of climate change, innovative technologies like floating solar offer hope and a path towards a greener and more resilient planet. We can conserve land resources, reduce water evaporation, and support the transition to a low-carbon solar energy landscape by harnessing the sun’s solar energy on water bodies. While challenges exist, continuous research, development, and global collaboration will pave the way for a brighter, renewable energy-powered future.
Embrace the future of renewable energy
Explore the potential of floating solar installations for your business or community with Energy Matters.
Energy Matters is one of Australia’s most trusted solar quotes due to our high customer satisfaction and industry recommendations. Our team of solar experts can help you get up to 3 FREE solar quotes from pre-qualified and vetted solar firms in your area. Let’s harness the power of the sun together!