On this page
In recent years, virtual power plants (VPPs) have gained popularity in Australia as a promising solution to manage the increasing demand for electricity and the growth of renewable energy. However, there are still many challenges that need to be addressed before VPPs can be widely adopted in the country.
However, with the growing demand for electricity and the increasing focus on sustainability, VPPs are likely to become an important part of the energy mix in Australia in the coming years. As more homes and businesses adopt renewable energy sources and the technology for VPPs improves, we can expect to see the widespread adoption of VPPs for demand response programs and grid balancing in Australia.
Energy Matters has been a leader in the renewable energy industry since 2005 and has helped over 40,000 Australian households in their journey to energy independence.
Let us discuss and choose the best quote that suits your needs and budget, and we can connect you with our trusted local solar installers in Melbourne, who will provide up to 3 FREE quotes for your home and business solar energy system. Get your free quotes today!
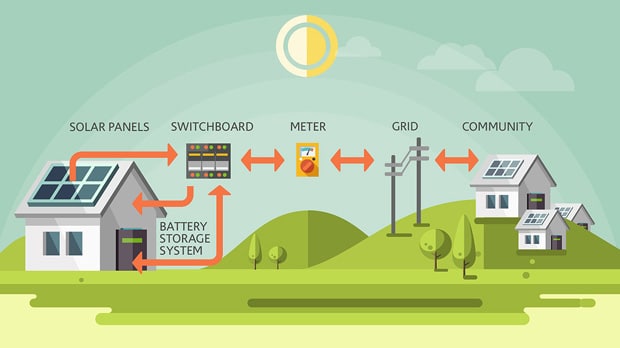
Virtual power plants and demand response
As the electricity demand continues to grow in Australia, so does the need for innovative solutions to meet this demand. One such solution is using virtual power plants (VPPs) for demand response programs and grid balancing during peak demand hours.
What are virtual power plants?
A virtual power plant is a network of distributed energy resources, such as solar panels, solar batteries, and other forms of renewable energy, that can be controlled and coordinated to act as a single entity. This allows VPPs to provide a range of services to the grid, including demand response programs and grid balancing.
Demand response programs
Demand response programs are designed to reduce electricity usage during peak demand hours, typically in the late afternoon or early evening when most people are at home and using appliances. VPPs can provide demand response by adjusting the electricity usage of individual homes or businesses within the network.
For example, a VPP could turn down the air conditioning in a group of homes for a short period during peak demand, reducing the strain on the grid and preventing the need for the construction of new power plants.
Grid balancing
VPPs can also be used for grid balancing by providing excess power to the grid during high demand and storing excess power during low demand. This helps smooth out grid fluctuations and prevent blackouts or brownouts.

Benefits of VPPs
There are several benefits to using VPPs for demand response programs and grid balancing in Australia in 2023. Firstly, they can help to reduce the need for new power plants and other infrastructure, which can be expensive and time-consuming to build.
Secondly, VPPs can provide a more reliable and stable electricity source by balancing out grid fluctuations. This can help to prevent blackouts and brownouts, which can be costly and disruptive for businesses and households.
Finally, VPPs can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by promoting the use of renewable energy sources. By providing a coordinated network of distributed energy resources, VPPs can help to make the grid more sustainable and reduce the reliance on fossil fuels.
Challenges and future outlook
Despite the benefits of VPPs, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for them to be widely adopted in Australia. These include the need for regulatory frameworks to support the use of VPPs and the need for investment in new infrastructure and technologies.
Regulatory issues
One of the major challenges facing the implementation of VPPs in Australia is regulatory issues. The current regulatory framework in Australia is designed to support traditional power plants, making it difficult for VPPs to enter the market. The existing regulations do not provide a clear pathway for VPPs, which creates uncertainty for investors and makes it difficult for VPPs to secure financing. Furthermore, there is a lack of uniformity in regulations across different states, which further complicates the regulatory environment for VPPs.
Market competition
Another significant challenge facing VPPs in Australia is market competition. The energy market in Australia is highly competitive, with a large number of traditional power plants competing for market share. VPPs will have to compete against these established players, which may prove challenging, especially for smaller VPPs. Moreover, the current market structure does not provide adequate incentives for VPPs to enter the market, making it difficult for them to compete on a level playing field.
Technology and infrastructure
The technology and infrastructure required for VPPs are still in the developmental phase. While VPPs have proven successful in small-scale pilot projects, scaling up to commercial levels will require significant investment in technology and infrastructure. The implementation of VPPs will require sophisticated software and hardware systems to manage the flow of electricity and ensure grid stability. Furthermore, the infrastructure required for VPPs, such as energy storage and distribution systems, will need to be expanded to support the increased demand for electricity.
Consumer awareness
One of the lesser-known challenges facing VPPs in Australia is consumer awareness. Many Australians are not aware of the benefits of VPPs and are unfamiliar with how they work. Educating consumers about the advantages of VPPs and their role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions will be critical for the widespread adoption of VPPs in Australia.
Experience a new level of energy savings with Energy Matters Marketplace – your one-stop shop for renewable energy products and more. Whether you’re looking for solar panels, battery storage or outdoor or indoor products. Check out the most popular products we offer and shop now!
Comparing virtual power plants to conventional power plants
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) are a relatively new concept in the power industry. A VPP is essentially a network of distributed energy resources (DERs) that can be controlled and coordinated to operate as a single entity. This means that solar panels, wind turbines, battery storage systems, and other DERs can be grouped together and managed through software to provide grid services to utilities and consumers. VPPs provide benefits such as improved energy efficiency, reduced energy costs, and increased grid stability.
On the other hand, traditional power plants are centralised power generation facilities that use a single source of fuel, such as coal or nuclear, to produce electricity. These plants are usually owned and operated by utility companies and are designed to supply large amounts of electricity to the grid. While they have been the backbone of the energy system for many years, traditional power plants have been criticised for their high carbon emissions and impact on the environment.
One of the main differences between VPPs and traditional power plants is their size and scale. Traditional power plants are large facilities that require significant infrastructure, equipment, and labour investment. VPPs, on the other hand, are made up of smaller, distributed resources that can be easily installed and integrated into the grid. This means that VPPs can be more cost-effective and flexible than traditional power plants.
Another significant difference between VPPs and traditional power plants is their fuel source. Traditional power plants rely on a single source of fuel, such as coal or nuclear, to generate electricity. VPPs, on the other hand, use a mix of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro. This means that VPPs produce less carbon emissions and are more sustainable than traditional power plants.
One similarity between VPPs and traditional power plants is their ability to provide grid services. Traditional power plants provide essential grid services such as frequency regulation, voltage control, and load balancing. VPPs can also provide these services and more, such as demand response and energy storage. However, VPPs have the added benefit of being able to do this more flexibly and efficiently than traditional power plants.
In terms of reliability, traditional power plants are generally considered to be more reliable than VPPs. This is because traditional power plants are designed to supply a consistent and stable electricity supply to the grid. At the same time, VPPs rely on distributed energy resources that may be subject to fluctuations in weather and other factors. However, advances in technology and software have made VPPs more reliable and efficient than ever.
Case Study: Virtual power plant implementation
Virtual power plants (VPPs) are becoming increasingly popular in the energy industry as a way to integrate renewable energy sources into the electricity grid. In Australia, a VPP project was implemented by AGL Energy, one of the country’s leading energy companies. This case study examines the success of AGL’s VPP project and its outcomes.
Background
AGL Energy’s VPP project was implemented in South Australia in 2017. The VPP consisted of a network of residential solar and battery systems, which were connected to AGL’s Virtual Power Plant platform. The VPP was designed to help balance the electricity grid during peak demand periods by allowing AGL to remotely control and dispatch energy stored in the batteries to the grid.
Implementation
AGL partnered with energy storage provider Sunverge to provide residential solar and battery systems for the VPP. The VPP initially started with a pilot program of 1,000 residential systems and was later expanded to include over 1,400 systems. The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) supported the project, which provided $5 million in funding.
Outcomes
AGL’s VPP project has been a success, with a number of positive outcomes. Firstly, the VPP has helped to improve grid stability and reliability during peak demand periods. By remotely dispatching stored energy from the residential battery systems, AGL has reduced strain on the grid during times of high demand, thereby preventing blackouts and other disruptions.
Secondly, the VPP has enabled the integration of more renewable energy into the grid. By utilising stored energy from the residential systems, AGL has been able to increase the amount of renewable energy in the grid without compromising on reliability. This has helped to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Finally, the VPP has provided benefits to the participating residential customers. Through the VPP platform, customers are able to receive payments for allowing their battery systems to be controlled by AGL during times of high demand. This has helped to offset the cost of installing and maintaining solar and battery systems, making them more accessible to a wider range of customers.
Still can’t afford to switch to solar power?
Are you considering getting solar panels but are currently short on funds? You can still invest wisely, and Energy Matters can help you.
Powow and Energy Matters have teamed up to provide consumers with an alternative to switching to solar power and battery storage.
The biggest obstacle to installing solar and battery storage is typically finance. With Powow’s PPA and VPP, our customers will have a $0 upfront option and financial stability in the uncertain energy market.
Get up to 3 obligation-free quotes by getting in touch with us right away. Find out what payment plan options suit your needs and budget!
Check out our page for Powow: Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) and Virtual Power Plant (VPP).











































