NSW officially launched the first tender of a ten-year NSW Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap program on Tuesday, 4th of October and an auction will be held every six months. A renewable energy and energy storage auction will replace the state’s retiring coal-fired power units. The final five coal-fired power plants in NSW are set to close in the following 11 years.

“NSW is targeting the construction of 12 gigawatts of renewable energy by 2030, enough to power the equivalent of 5.8 million homes, as well as 2 gigawatts of long-duration storage like pumped hydro, making this the biggest renewable energy policy in Australia’s history,” Minister of Energy, Matt Kean said.
“The opening of the first tender marks a major milestone in delivering our renewable energy and storage plans, and it’s expected to create a jobs and investment boom across NSW.”
“Putin’s illegal invasion of Ukraine has put enormous pressure on power prices and shows why we need to fast track our plans to replace ageing power stations and reduce our reliance on the generation that relies on volatile international commodity prices.”
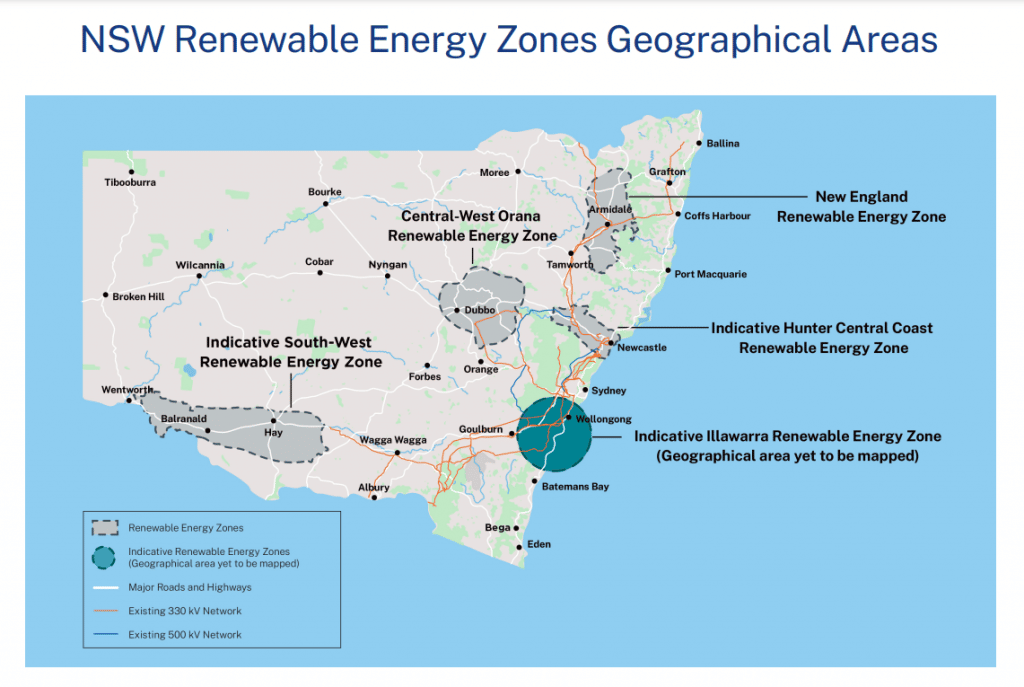
The Central-West Orana Renewable Energy Zone (REZ), located in the area surrounding Dubbo in the state’s northwest, is the focus of the first tender round, which is still open until October 28.
The participation of “sufficiently advanced projects” from across NSW, that connect to the current transmission system is also welcomed, according to AEMO Services.
The first five Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) approximate positions are shown on the map below.
Why was the Central-West Orana Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) chosen?
The Central-West Orana REZ, in the territory of the Wiradjuri, Wailwan, and Kamilaroi people, is around 20,000 square kilometres in size and is centred on the communities of Dubbo and Dunedoo.
The REZ geographic boundaries have since been improved by EnergyCo based on new research and input from important stakeholders, including discussions and fact-checking with the CWO Regional Reference Group and REZ Technical and Commercial Steering Group. In addition, the NSW Government conducted a thorough statewide geospatial mapping exercise in 2018, selecting the Central-West Orana Renewable Energy Zone’s (REZ) suggested site. Using areas with high potential for renewable energy resources, proximity to the existing electrical grid and consideration of potential interactions with other current land uses, such as agricultural lands and biodiversity preservation, this initial analysis sought to determine the most suitable locations to accommodate renewable energy generation throughout the State.
The Draft 2022 Integrated System Plan from the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) also recognises the significance of the Central-West Orana REZ (ISP).
What is the Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap?
The NSW Government’s strategy to improve the energy industry’s cheaper, cleaner and more reliable energy is called the Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap (the Roadmap). By 2030, it lays out a coordinated plan to generate at least 12 gigawatts of renewable energy and install two gigawatts of long-term storage.
The Roadmap is expected to:
- Attract up to $32 billion in private investment for regional energy infrastructure by 2030.
- Support 6,300 construction jobs and 2,800 ongoing jobs, mostly in regional NSW.
- Save around $130 a year on the average NSW household electricity bill and $430 a year on the average small business electricity bill between 2023 and 2042 compared if the Roadmap is not implemented.
- Reduce NSW electricity emissions by 90 million tonnes by 2030.
The Electricity Infrastructure Investment Act 2020, enacted into law in December 2020 with broad support, provides the framework for the Roadmap. The Roadmap organises investments in transmission, generation, storage, and strengthening infrastructure as ageing coal-fired generating plants are shut down. The Roadmap outlines initiatives to cooperate to bring about “whole-of-system” advantages.
Watch a short video explainer on the Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap
NSW plans and progress
Currently, the capacity of NSW to produce renewable energy is about 13,500 megawatts (MW), or about 53% of the state’s total generation capacity.
The total generation capacity includes generations from
- large-scale and rooftop solar power panels
- hydropower stations
- wind power stations
- biomass power stations.
The NSW Government’s Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap has contributed to this increase in renewable energy. The Roadmap is expected to be between 2023 and 2040.
The traditional, one-way energy system, which was predominately powered by massive, centralised coal and gas-fired power plants, is evolving. The transition to a two-way energy system is underway. More homes and businesses are installing individual rooftop solar power systems and sending electricity back to the grid.
Communities are looking to innovative local renewable energy technologies and models to lower energy costs and stabilise the grid. Also, the initial investment significantly reduces electricity bills thanks to generous government incentives and rebates.
Electric cars, which consume and store energy, are becoming increasingly popular. It will help ensure there is a supply for these vehicles when it’s required. Energy demand peak can be reduced by managing demand and identifying non-critical usage.
Partners delivering the Roadmap
Energy Corporation of NSW (EnergyCo) is one of several important organisations that the NSW Government formed to implement the Electricity Infrastructure Roadmap, along with the following collaboration with entities and other key organisations.
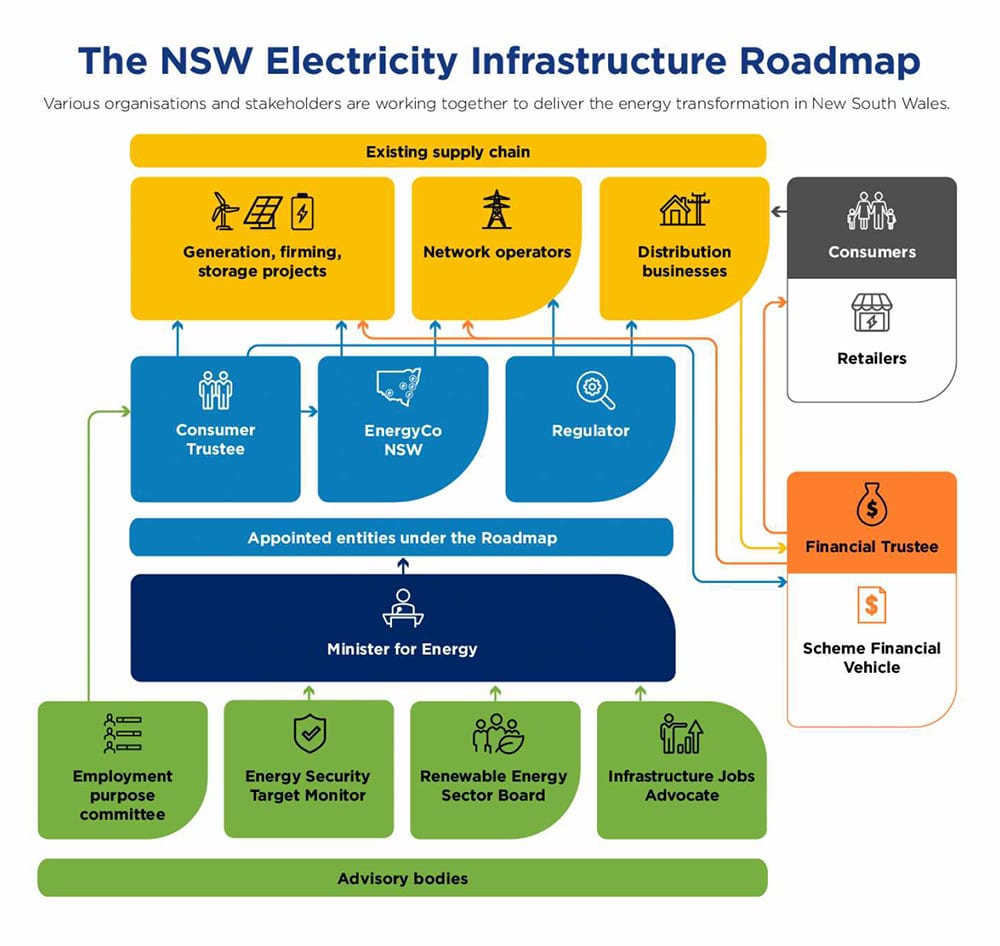
- The Consumer Trustee: Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) Service
- The Regulator: Australian Energy Regulator (AER)
- The Renewable Energy Sector Board
- Electricity Infrastructure Jobs Advocate (Jobs Advocate)
- Transmission Network Service Provider: Transgrid
- Distribution Network Service Providers (DNSPs): Ausgrid, Essential Energy and Endeavour Energy sector