Queensland University of Technology (QUT) and Japan’s Sumitomo Electric Industries (SEI) have inked a partnership for a concentrated solar photovoltaic (CPV) demonstration project in in the state; which will include energy storage at a later date.
“Our partnership with Sumitomo Electric gives us the opportunity to study the operation of large-scale renewable energy generation and storage technologies in Queensland’s climate,” said QUT’s Professor Ian Mackinnon.
CPV involves a layer of lenses placed above special solar cells to focus the sun’s energy. The technology is around 2.5 times more efficient than conventional solar panels.
This won’t be Sumitomo’s first CPV rodeo. The company has constructed a number of projects around the world and recently completed a 1 MW CPV generation plant in Morocco.
Queensland Premier Annastacia Palaszczuk welcomed partnership the announcement.
The proposed project will assess a total energy solution for off-grid communities including battery storage and energy management systems,” Ms Palaszczuk said.
“SEI also plan to undertake local production of their battery storage system as they find more opportunities in off-grid areas of Queensland.”
The energy storage to be implemented at a later date will be based on a redox flow battery system, which Professor Mackinnon believes will be a crucial part of the energy mix both in Australia and throughout the world.
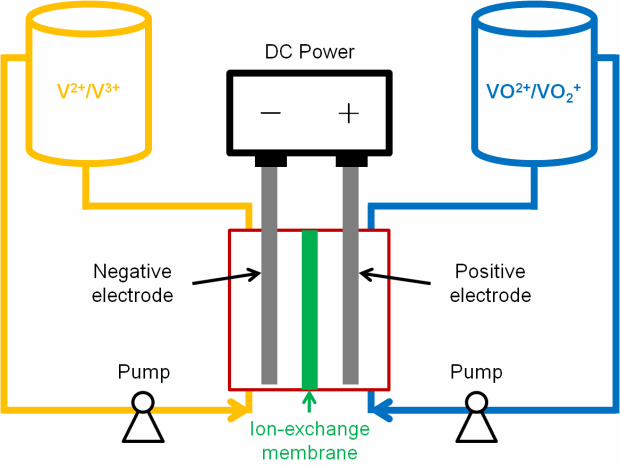
Various types of redox flow battery chemistry technologies exist, but essentially they all consist of two chemical components dissolved in liquids separated by a membrane and some other whizz-bang componentry. When electricity is needed, the two liquids are pumped into a central stack and as ions pass through a selective membrane, energy is produced. The battery is ‘recharged’ by reversing the flow.
The following image (hat tip to Xing Xie) shows the basics of such a battery, this one based on a vanadium chemical solution. Currently, flow batteries are most common in larger scale storage systems and can be easily scaled up to megawatt capacities.
It’s hoped the ongoing partnership will see other research being carried out, including in advanced automotive systems, advanced materials and superconductivity.
Professor Mackinnon acknowledged the assistance of the Trade & Investment Queensland (TIQ) Japan team for their role in assisting the partnership becoming a reality.












































