Coal and solar energy share similarities and differences as global energy sources in terms of having tremendous effects on the environment, the world’s economic standing, how we financially benefit from them, and human health.
Energy Matters offers FREE solar quotes, providing a non-committal opportunity for those interested in understanding the practical aspects and potential benefits of integrating solar solutions into their energy portfolios. This insight can contribute to a more comprehensive evaluation of sustainable energy options within the broader context of global energy dynamics.
At a glance: Fossil fuels vs renewable energy sources
For the time being, most consumers use fossil fuels because they are inexpensive and convenient. Experts do not believe fossil fuels to be renewable energy because their global supply is limited. Solar energy, on the other hand, is a truly renewable natural energy source.
Solar energy is a renewable energy source that will not deplete over time. One hour of sunlight delivers more energy than humanity consumes in a year. We can rest assured that the sun will always shine.
On the other hand, fossil fuels, such as coal, petroleum or oil, and natural gas, are non-renewable energy sources that require millions of years to refill.
Renewable energy is derived from natural resources that can be replenished throughout a typical human lifetime and include the following types of power:
- Solar
- Wind
- Hydro
- Tidal
- Geothermal
- Biomass
- Hydrogen
Visit our page to learn more about each type of renewable energy source.
Fossil fuels can take millions of years to replenish naturally. The most commonly used fossil fuels are:
- Natural gas
- Coal
- Oil/petroleum

Coal
Coal is non-renewable but valuable fossil fuel because it provides a consistent source of electricity, which is required for steel production.
Coal is a rock near the earth’s surface, one of the most abundant fossil fuels on the planet. It is extracted via surface mining (using machinery to remove the topmost layers of rock and soil) and underground mining (using machines and miners to remove deep coal underground).
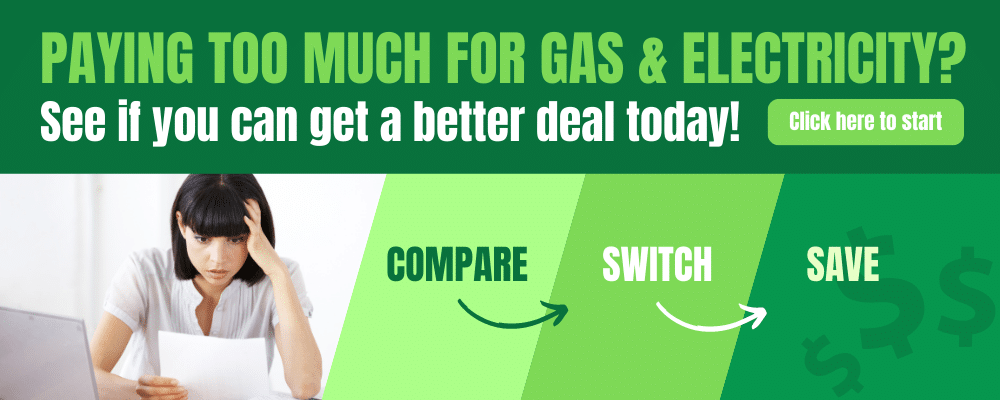
Brown and black coal are mostly used as fuel sources for power plants. Because burning coal generates heat, which is then used to generate steam, the coal is also known as thermal or steam coal. The steam turns turbines to generate energy.
Australia has abundant black and brown coal resources. The Bowen-Surat (Queensland) and Sydney basins have the most substantial black coal resources (New South Wales). Australia’s largest commodity export is coal, valued at more than $40 billion in yearly thermal and metallurgical coal exports, primarily to Japan, India, the European Union, the Republic of Korea, and Taiwan.
The vast majority of Australia’s brown coal resources are concentrated in the Gippsland Basin in Victoria, which is used to generate electricity. Nearly 500 years of brown coal resources remain at current production rates[2].
Solar energy
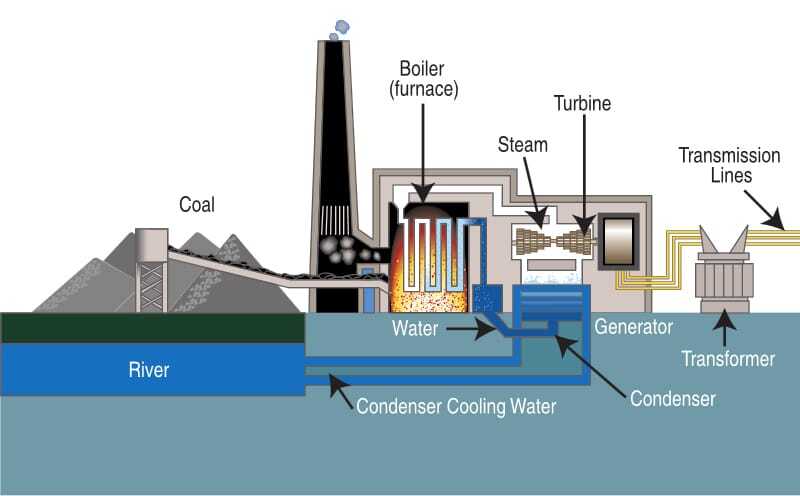
The sun’s energy is captured using various technologies, and new ones are continuously being developed. Among the most notable are solar photovoltaic and solar thermal. Solar thermal systems transform solar energy into heat, or thermal energy, which can use for various things, such as producing steam to power an electricity generator. This energy can cause a refrigeration cycle to provide solar-based cooling.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems use solar panels containing solar cells that convert sunlight directly into electricity when exposed to sunlight. Glass, aluminium, silicon, and tin make solar panels. Other electrical devices also contain rare metals, such as indium, gallium, and germanium. These rare metals account for only around 1% of the panel volume yet have the most significant environmental impact. Check out our page for solar panels and best solar panel brands in Australia.
Solar power is harnessed in solar panels, which store solar electricity and are stored in solar storage batteries. Batteries have a steady electrical power supply that supplies power before sunset or compensates for power consumption.
Energy Matters can assist you in choosing the best solution for a solar battery’s suitability using our Solar Power and Battery Storage Calculator.

Australia has some of the best solar resources in the world due to high amounts of solar radiation over wide areas. The best solar resources are mostly concentrated in Australia’s northwest and centre, often in places without access to the electricity grid and far from major population centres and important energy markets.
Solar lifetime environmental impacts compared to coal
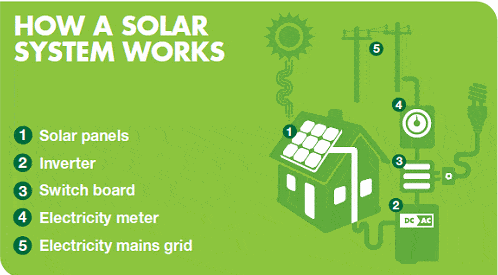
Solar is approximately 20 times more environmentally friendly per kilowatt-hour (kWh) generated than coal.
- Solar: between 45 – 54 grams CO2e/kWh generated
- Wind: between 11 – 13 grams CO2e/kWh generated
- Coal: between 975 – 1,050 grams CO2e/kWh generated
- Natural Gas: between 465 – 475 grams CO2e/kWh generated[5]
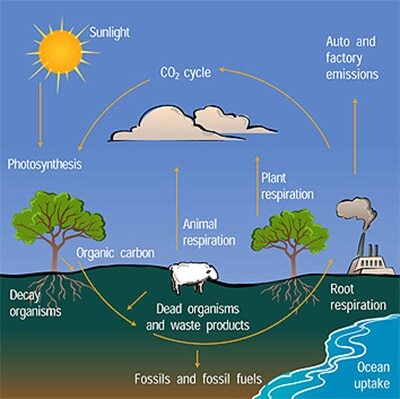
The power generation requirement for coal is around 700 grams per hour, and it releases several pollutants into the atmosphere, including heavy metals. This has far more damaging health effects than solar energy and requires less than a kilogram of power for every kW produced.
Advantages and disadvantages of solar and coal
There are numerous advantages and disadvantages to solar energy and coal. Both significantly impact the environment, the energy sector, daily life, and the destiny of civilisation.
The major benefit of coal is our advanced technology for converting it into energy. Nonrenewable fossil fuel energy has historically been abundant and widely used worldwide. We’ve had millennia to refine our technique.
While coal will not run out in the next 50 years, solar energy is already here and will never run out.
While solar energy will never run out, it is not available consistently. Solar panels are inefficient when cloudy weather, just as wind turbines do not spin with no wind.

However, solar energy is cleaner than coal, so it does not contaminate the environment. We must end pollution and global warming if we want humankind to outlive nonrenewable energy sources.
The contrast is much more pronounced when we compare coal pollution to solar energy pollution. And many people are unaware that fossil fuels not only emit greenhouse gas emissions, but the drilling process also destroys and erodes the earth and pollutes the water supply.
Check out our page to learn more about coal power vs solar power: which is more efficient.
Solar can cost less than coal
The construction or installation of the roof of solar power stations requires substantial investment. In its lifetime, it produces more kilowatts compared with coal. But the structure of the power plant will take a long time. More than half the carbon produced from electricity from coal is made in the first year. Almost the same situation applies to tonnes of mined material.
Solar energy is now just as economical as coal energy, if not cheaper in some circumstances. Some solar panel systems can even generate electricity for less than half the cost of coal. That’s a lot of money that could be saved. Furthermore, solar energy is becoming more affordable thanks to several rebates and generous feed-in tariffs.
Given the rate of coal consumption, the world is approaching a point when we will have the little option – coal is being mined far faster than the replenishment rate. As a result, coal is expected to be more expensive than solar within the next decade.
These statistics cover all electricity generation in Australia, including by power plants and by businesses and households for their use.

| Year | Black Coal | Brown Coal | Solar |
| 2009-10 | 51.5% (124,478) | 23.2% (55,968) | 0.1% (278) |
| 2010-11 | 46.3% (116,949) | 21.9% (55,298) | 0.3% (850) |
| 2011-12 | 47.4% (120,302) | 21.7% (55,060) | 0.6% (1,489) |
| 2012-13 | 44.8% (111,491) | 19.1% (47,555) | 1.5% (3,817) |
| 2013-14 | 42.6% (105,772.4) | 18.6% (46,076.2) | 2.0% (4,857.5) |
| 2014-15 | 42.7% (107,639) | 20.2% (50,970) | 2.4% (5,968) |
| 2015-16 | 44.4% (114,295) | 16.9% (43,558) | 2.7% (6,838) |
| 2016-17 | 45.8% (118,272) | 13.8% (36,008) | 3.1% (8,072) |
| 2017-18 | 46.6% (121,702) | 13.8% (36,008) | 3.8% (9,930) |
| 2018-19 | 45.4% (119,845) | 13.1% (34,460) | 5.6% (14,849) |
| 2019-20 | 42.2% (111,873) | 12.7% (33,649) | 7.9% (21,033) |
| 2020-21 | 40.0% (106,251) | 12.8% (34,060) | 10.4% (27,717) |
| Source: Wikipedia[1] | |||
The clear distinction between solar is that coal is the material mined. However, other aspects contribute to its method. This includes the following[4]:
| Coal | Solar Panel |
|---|---|
| Mining | Raw Materials Extraction |
| Power Plant Construction | Materials Production |
| Preparation | Module Manufacture |
| Transport | System/Plant Component Manufacture |
| Combustion | Installation/Plant Construction |
| Power plant operation and maintenance | Power Generation |
| Power plant decommissioning | System/Plan Operation and Maintenance |
| Waste disposal | System/Plant Decommission |
| Disposal |
Coal phase-out in Australia
Coal combustion is the most significant contributor to climate pollution in Australia, accounting for more than a quarter of total greenhouse gases. Victoria also has the dirtiest power plants in the country due to the use of brown coal. They provide roughly 40% of the state’s climate pollution.
To protect the communities and avoid the worst effects of climate change, Victoria has begun closing all coal-fired power plants over the next decade and replacing them with sustainable energy sources such as solar, wind, batteries, etc.
Emission reduction targets and other state government programmes have resulted in a massive increase in renewable energy. In 2019-20, clean energy sources provided 25% of Victoria’s electricity. The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) anticipated in 2021 that all coal power facilities in Victoria will likely cease by 2032[3] like AGL is phasing out coal in 2035.
Why does the gap between coal and technology matter?
The advantages of solar energy over coal provide a broad list of reasons for a house or commercial property owner to consider.
Solar energy is the better alternative to the environmental impact of solar electricity versus fossil fuels like coal. For perceived reliability, many consumers choose fossil fuels; oil, coal, and natural gas have a higher energy density (the amount of stored energy per unit volume) than solar energy.
The solar industry is already on its way to addressing these obstacles, thanks to enhanced research and development to better PV technology and more innovative software to connect customers and suppliers.

On the other hand, investing in a battery for solar storage allows you to tap into energy even when the sun isn’t shining and helps give predictability. While electric vehicles (EVs) do not destroy the environment the same way as combustion engines, they still require charging.
Energy Matters has been a leader in the renewable energy industry since 2005. We can connect you with our trusted local installers, who will provide up to 3 FREE solar quotes for your home and business solar energy system. Complete our quick quiz and begin your solar journey today!
References:
[1] Wikipedia: Energy in Australia [2] Australian Government Geoscience Australia: Energy Overview [3] Environmental Victoria: Victoria Beyond Coal [4] Climate Solution Center: Are Solar Panels Better than Coal?